IAEA mission says main challenge is PAA’s independence.
Poland’s nuclear regulatory framework is in line with International Atomic Energy Agency safety standards and its regulatory body is competent and “prepared for the launch” of the country’s ambitious nuclear power programme, the International Atomic Energy Agency said.
A 12-day Integrated Regulatory Review Service (IRRS) mission to Poland, conducted at the request of the Polish government, said regulator Panstwowa Agencja Atomistyki (PAA) is a competent regulatory body whose staff are committed to deliver their regulatory statutory obligations effectively and to prepare to embark on a nuclear power programme in line with international safety standards.
It said the main challenge in Poland is to “implement robust measures to ensure that the PAA is effectively independent and continues to be properly resourced”.
Using IAEA safety standards and international good practices, IRRS missions are designed to strengthen the effectiveness of the national regulatory infrastructure for nuclear and radiation safety.
“This is a major milestone for Poland, which has been considering a nuclear power programme for many years,” said Mike King, deputy office director for reactor safety programs and mission support at the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the IRRS team leader.
King said the PAA’s commitment to safety is essential to ensuring that any nuclear power plants built in Poland are operated safely and securely.
The mission – the second of its kind – said Poland has trained 300 regional sanitary inspectorate staff on how to inform the public on radon related issues.
IAEA Praises Communications Strategy
PAA has a communications strategy that allows it interact effectively with interested parties, including information published on its website in relation to the conflict in neighbouring Ukraine, the mission said.
It said Poland has installed 30 additional radiation monitoring stations close to its border to improve radioactivity detection capability.
Poland operates a single research reactor, Maria, has a research reactor, EWA, under decommissioning and two spent fuel storage facilities, all in Otwock, near Warsaw.
The National Radioactive Waste Repository in the town of Rozan is a near-surface repository for radioactive waste and sealed radioactive sources disposal operated by Radioactive Waste Management Plant.
The IAEA said industry, medicine and research applications of radioactive sources are widely used.
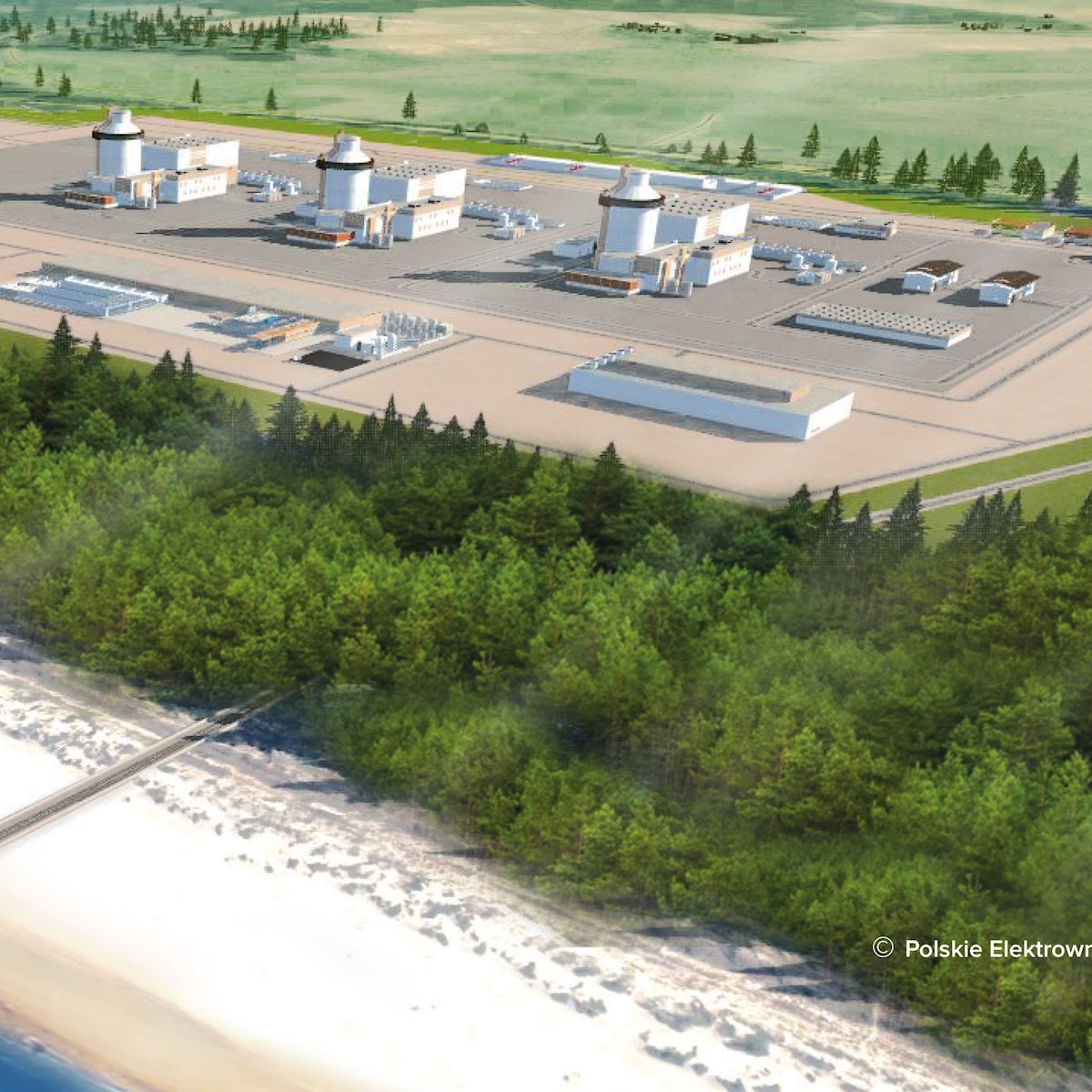
Poland has plans to build large-scale nuclear power plants and small modular reactors in an effort to reduce carbon emissions from its power generation sector. The country at present gets about 70% of its electricity from stations burning black and brown coal.
In November 2022, Warsaw chose US-based Westinghouse Electric to supply its AP1000 reactor technology for a three-unit nuclear power station at the Lubiatowo-Kopalino site in the municipality of Choczewo near the Baltic coast of Pomerania.
The first AP1000 unit is expected online in 2033 with others planned to follow into the 2040s.